PlexPlus®
PlexPlus® is a next generation qPCR technology which doubles the multiplexing capacity of standard installed instruments. This is achieved by detecting multiple targets within each fluorescence channel using universal, Low- and High-temperature PlexPlus® Probes, which are switched on or off during PCR cycling. Target-dependent fluorescence is acquired at two temperatures across multiple wavelengths in real time with no cross talk between temperatures.
PlexZyme®
High performance and reliable multiplex qPCR detection. PlexZyme® is the driver behind the entire SpeeDx product portfolio.
Sensitive and Quantitative
Can detect less than 10 copies of target and has a good dynamic range from 106 to 10 copies.Highly Specific
Specificity is determined by 5 binding events of the 2 primers and 2 partzymes to the amplicons, plus probe for signal generation.Flexible
Probe design is independent of target sequence, allowing for the use of a suite of well-characterised universal probes.PlexZyme® technology offers high performance and reliable qPCR detection and is the driver behind the entire SpeeDx product portfolio. During PlexZyme® qPCR, primers amplify target nucleic acid sequences and produce amplicons which serve as a template for PlexZyme® formation. Once the partzymes have assembled into PlexZyme® enzymes, universal probes bind and enzymatic cleavage of the probes between fluorophore and quencher dye pairs generates fluorescence. Changes in fluorescence allow detection and/or quantification of the target nucleic acid in real time.
PlexPrime®
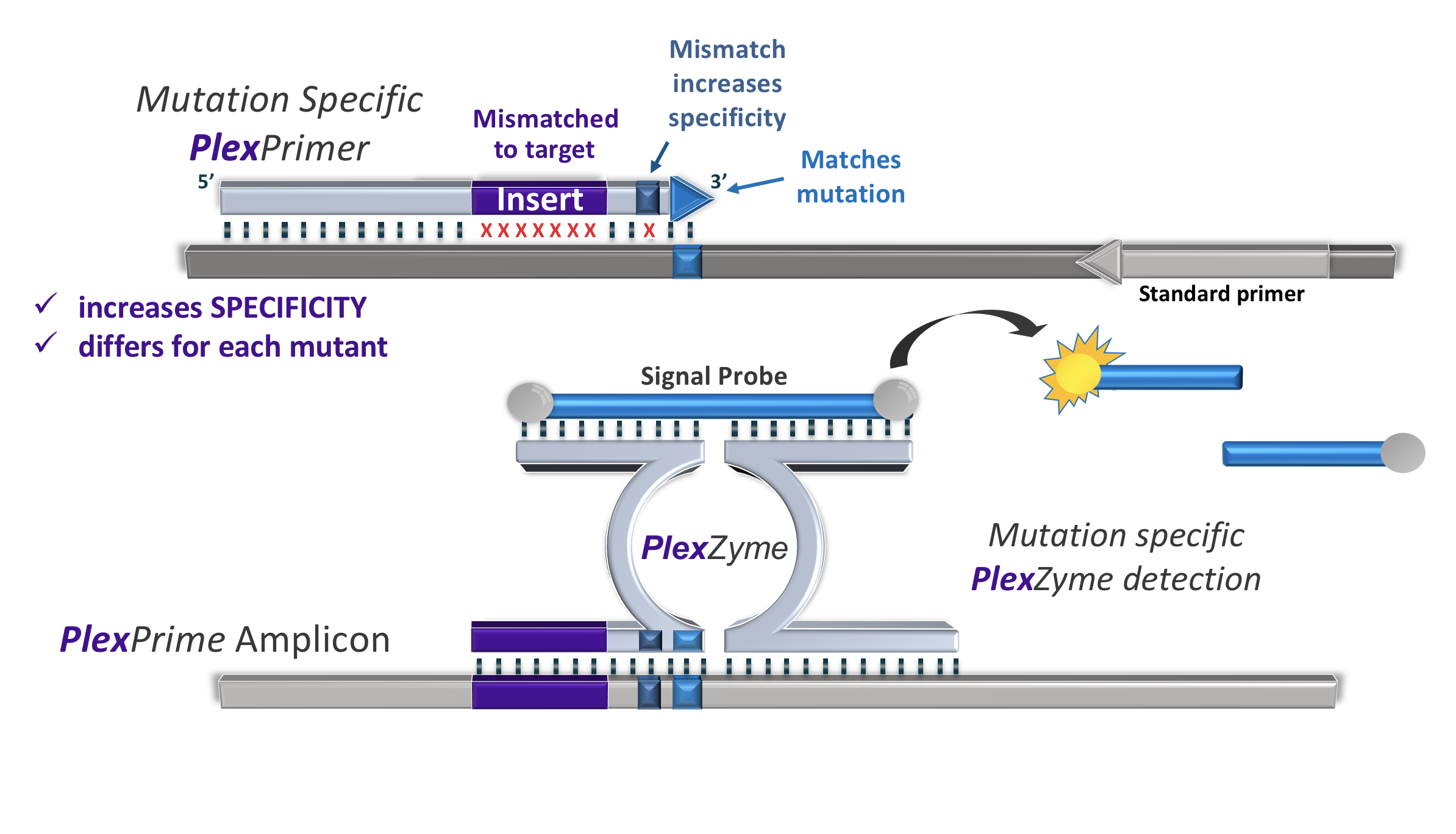
Novel nucleic acid amplification approach, creating amplicons distinctly different from the parent sequence. The combination of PlexPrime® and PlexZyme® technology enables multiplex mutation detection with high sensitivity and specificity.
Multiplex compatible
Detect multiple mutations in a single reaction.Versatile
Flexibility for challenging sequences.Highly Specific
Increased stringency due to insert sequenceThe PlexPrime® primer is composed of three regions:
- 5’ region anchors the primer to a particular location in the target
- 3’ region selectively amplifies the target sequence of interest
- the Insert, acting as a bridging structure which both (a) inserts target-independent sequence into the resulting amplicon and (b) increases the selective pressure of the 3’ region
The unique feature of the PlexPrime® primer make it extremely suitable for detection and discrimination of mutations or Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) in a multiplex reaction or a pool of nucleic acid sequences containing non-conserved regions.
References
Mokany E., Tan Y.L., Bone S.M., Fuery C., Todd A.V., 2013. MNAzyme qPCR with superior multiplexing capacity. Clin. Chem. 59(2); 419-426
Link | Article | Supplementary Information
Mokany E., Bone S.M., Young P.E., Doan T.M., Todd A.V., 2010. MNAzymes are a versatile new class of nucleic acid enzymes which can function as biosensors and molecular switches. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132(3); 1051-1059
Link | Article | Supplementary Information
Tan L. Y., Walker S. M., Lonergan T., Lima N. E., Todd A. V. Mokany E. 2017. Superior Multiplexing Capacity of PlexPrimers Enables Sensitive and Specific Detection of SNPs and Cluster Mutations in qPCR. PLOS One January 23rd.
Link